Difference between application software and system software
Software
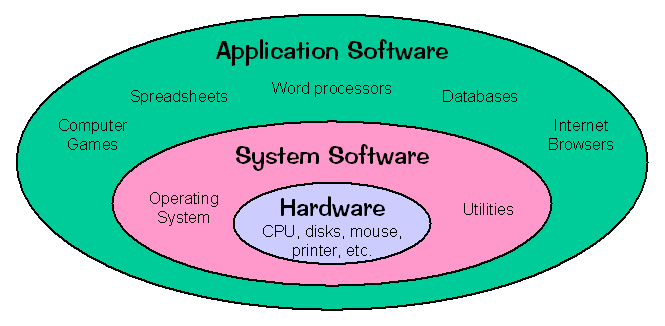
- Software is a generic term for organized collections of computer data and instructions, often broken into two major categories: system software that provides the basic nontask-specific functions of the computer, and application software which is used by users to accomplish specific tasks.
System software
- System software is used for operating computer hardware.
- System software is responsible for controlling, integrating, and managing the individual hardware components of a computer system so that other software and the users of the system see it as a functional unit without having to be concerned with the low-level details such as transferring data from memory to disk, or rendering text onto a display.
- Generally, system software consists of an operating system and some fundamental utilities such as disk formatters, file managers, display managers, text editors, user authentication (login) and management tools, and networking and device control software.
- Generally, users do not interact with system software as it works in the background.
Example:
- Microsoft Windows
- Linux
- Unix
- Mac OSX
- DOS
Application software
- Application software is used to accomplish specific tasks other than just running the computer system.
- Application software may consist of a single program, such as an image viewer; a small collection of programs (often called a software package) that work closely together to accomplish a task, such as a spreadsheet or text processing system; a larger collection (often called a software suite) of related but independent programs and packages that have a common user interface or shared data format, such as Microsoft Office, which consists of closely integrated word processor, spreadsheet, database, etc.; or a software system, such as a database management system, which is a collection of fundamental programs that may provide some service to a variety of other independent applications.
- Users always interact with application software while doing different activities.
Example:
- Opera (Web Browser)
- Microsoft Word (Word Processing)
- Microsoft Excel (Spreadsheet software)
- MySQL (Database Software)
- Microsoft PowerPoint (Presentation Software)
- Adobe Photoshop (Graphics Software)