Recursion in c Programming
- When function is called within the same function, it is known as recursion in C.
- In programming, there might be a situation where a function needs to invoke itself.
- The C language supports recursive feature, i.e. a function is called repetitively by itself. The recursion can be used directly or indirectly.
- The direct recursion function calls to itself till the condition is true. In indirect recursion, a function calls another function, then the called function calls the calling function.
Types of Recursion
There are two types of Recursion
- Direct recursion
- Indirect recursion
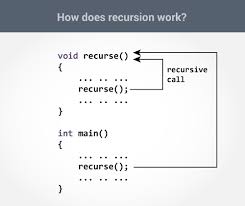
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int x,s;
void main(int);
void main(x)
{
s=s+x;
printf("\n x = %d s = %d",x,s);
if(x==5)
exit(0);
main(++x);
}
Output:
x = 1 s = 1 x = 2 s = 3 x = 3 s = 6 x = 4 s= 10 x = 5 s= 15
Disadvantages of Recursion
- It consumes more storage space the recursive calls along with automatic variables are stored on the stack.
- The computer may run out of memory if the recursive calls are not checked.
- It is not more efficient in terms of speed and execution time.
- According to some computer professionals, recursion does not offer any concrete advantage over non-recursive procedures/functions.
- Recursive solution is always logical and it is very difficult to trace.(debug and understand).
- In recursive we must have an if statement somewhere to force the function to return without the recursive call being executed, otherwise the function will never return.
- Recursion takes a lot of stack space, usually not considerable when the program is small and running on a PC.
- Recursion uses more processor time.
- Recursion is not advocated when the problem can be through iteration.
- Recursion may be treated as a software tool to be applied carefully and selectively.