Pointer in C++ language
- A pointer is an object that contains a memory address.
- Typically, a pointer is used to access the value of another object.
- Often this other object is an array. In fact, pointers and arrays are related to each other more than you might expect.
- The pointer is one of C++’s most powerful features. It is also one of its most troublesome.
- Despite their potential for misuse, pointers are a crucial part of C++ programming.
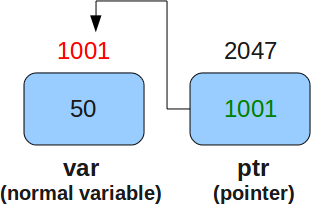
Pointer variable declaration
- A pointer is an object that contains a memory address.
- Very often this address is the location of another object, such as a variable. For example, if x contains the address of y, then x is said to “point to” y.
Syntax
type *var-name; //Here, type is the pointer’s base type.
int *ip;
The Pointer Operators
- There are two special operators that are used with pointers: * and &. The & is a unary operator that returns the memory address of its operand.
ptr = &total;
- The second operator is *, and it is the complement of &. It is a unary operator that returns the value of the variable located at the address specified by its operand.
val = *ptr;
Example
#include using namespace std;
int main()
{
int total;
int *ptr;
int val;
total = 3200; // assign 3,200 to total
ptr = &total; // get address of total
val = *ptr; // get value at that address
cout << "Total is: " << val << '
';
return 0;
}
