Array in Java
- An array is a collection of similar data types.
- Array is a container object that hold values of homogenous type. It is also known as static data structure because size of an array must be specified at the time of its declaration.
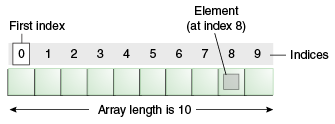
- Index of array starts from zero to size-1.
- An array can be either primitive or reference type. It gets memory in heap area
- An array is a collection of multiple elements which has same type of data.
- Array stores homogeneous (same data type) data contiguously in memory, and that too under one variable name, i.e. single name is assigned to the entire array elements.
- It stores either all integers or all floating point numbers or all characters.
- An array is a data structure used to process multiple elements with the same data type when a number of such elements are known.
- Arrays form an important part of almost all-programming languages.
- It provides a powerful feature and can be used as such or can be used to form complex data structures like stacks and queues.
- An array can be defined as an infinite collection of homogeneous(similar type) elements.
- This means that an array can store either all integers, all floating point numbers, all characters, or any other complex data type, but all of same type.
- Arrays are always stored in consecutive memory locations.
Features of Array
- It is always indexed. Index begins from 0.
- It is a collection of similar data types.
- It occupies a contiguous memory location
Flow Diagram
Array Declaration
Syntax-
datatype identifier[]; OR datatype[] identifier;
Example
int[] a; float[] a; char[] a; short[] a; int[][] a;
Initialization of Array
We used new operator to initialize an array.
int a[] =new int[5];
or
int a[]={2,3,4,5,6};
Accessing Array Element
In arrays, we can access the specific element by its index within square brackets.
Example
store[1]=5;
Multidimensional Array
- Multidimensional arrays are arrays of arrays.
- Two dimensional arrays are also called table or matrix, two dimensional arrays have two subscripts.
- Two dimensional array inwhich elements are stored column by column is called as column major matrix.
- Two dimensional array in which elements are stored row by row is called as row majo rmatrix.
- First subscript denotes number of rows and second subscript denotes the number of columns.
- The simplest form of the Multi Dimensionl Array is the Two Dimensionl Array. A Multi Dimensionl Array is essence a list of One Dimensionl Arrays.
Array Declaration
int a[][] =new int[4][5];
or
int[][] a={{2,3,4,5,6}{7,8,9,10,1}};
Accessing Array Element
For specifying both row and column in array,index start with 0.
Syntax-
arrayname[n-1][m-1];
Example
arrayname[2][3]=5;