Recursion in data structures
- Recursion is one of the most powerful tools in a programming language, but one of the most threatening topics-as most of the beginners and not surprising to even experienced students feel.
- When function is called within the same function, it is known as recursion in C. The function which calls the same function, is known as recursive function.
- Recursion is defined as defining anything in terms of itself. Recursion is used to solve problems involving iterations, in reverse order.
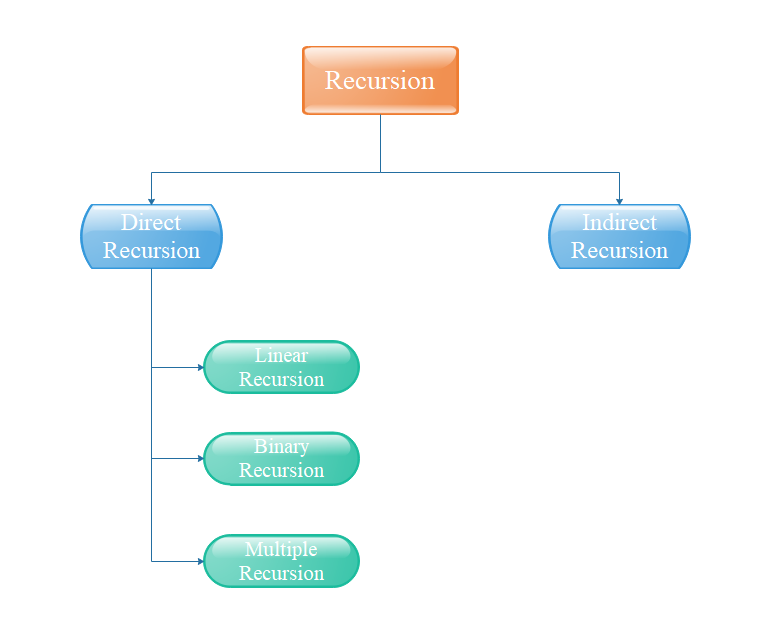
Types of Recursion
There are two types of Recursion
- Direct recursion
- Indirect recursion
Direct Recursion
When in the body of a method there is a call to the same method, we say that the method is directly recursive.
There are three types of Direct Recursion
- Linear Recursion
- Binary Recursion
- Multiple Recursion
Linear Recursion
- Linear recursion begins by testing for a set of base cases there should be at least one.
In Linear recursion we follow as under :
- Perform a single recursive call. This recursive step may involve a test that decides which of several possible recursive calls to make, but it should ultimately choose to make just one of these calls each time we perform this step.
- Define each possible recursion call, so that it makes progress towards a base case.
Binary Recursion
- Binary recursion occurs whenever there are two recursive calls for each non base case.
Multiple Recursion
- In multiple recursion we make not just one or two but many recursive calls.
//C program for GCD using recursion
#include int
Find_GCD(int, int);
void main()
{
int n1, n2, gcd;
scanf(“%d %d”,&n1, &n2);
gcd = Find_GCD(n1, &n2);
printf(“GCD of %d and %d is %d”, n1, n2, gcd);
}
int Find_GCD(int m, int n)
{
int gcdVal;
if(n>m)
{
gcdVal = Find_GCD(n,m);
}
else if(n==0)
{
gcdVal = m;
}
else
{
gcdVal = Find_GCD(n, m%n);
}
return(gcdVal);
}
Disadvantages of Recursion
- It consumes more storage space the recursive calls along with automatic variables are stored on the stack.
- The computer may run out of memory if the recursive calls are not checked.
- It is not more efficient in terms of speed and execution time.
- According to some computer professionals, recursion does not offer any concrete advantage over non-recursive procedures/functions.
- Recursive solution is always logical and it is very difficult to trace.(debug and understand).
- In recursive we must have an if statement somewhere to force the function to return without the recursive call being executed, otherwise the function will never return.
- Recursion takes a lot of stack space, usually not considerable when the program is small and running on a PC.
- Recursion uses more processor time.
- Recursion is not advocated when the problem can be through iteration.
- Recursion may be treated as a software tool to be applied carefully and selectively.
Difference between recursion and iteration
| Iteration | Recursion |
| In iteration,a problem is converted into a train of steps that are finished one at a time, one after another | Recursion is like piling all of those steps on top of each other and then quashing the mall into the solution. |
| With iteration,each step clearly leads on to the next, like stepping stones across a river | In recursion, each step replicates itself at a smaller scale, so that all of them combined together eventually solve the problem. |
| Any iterative problem is solved recursively | Not all recursive problem can solved by iteration |
| It does not use Stack | It uses Stack |