switch statement in c
The control statement that allows us to make a decision from the number of choices is called a switch, or more correctly a switchcase-default, since these three keywords go together to make up the control statement.
A switch statement allows a variable to be tested for equality against a list of values. Each value is called a case, and the variable being switched on is checked for each switch case.
Syntax of Switch Statement:
switch(integer expression)
{
case constant 1 :
do this ;
case constant 2 :
do this ;
case constant 3 :
do this ;
default :
do this ;
}
Flow Diagram
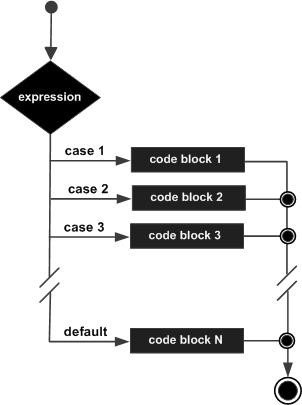
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 3;
switch( i )
{
case 1:
printf(" OK ");
case 2:
printf(" Hello ");
case 3:
printf(" Hi ");
default:
printf(" Bye ");
}
Output:
Hi
Break Statement:
The switch statement executes the case where a match is found and all the subsequent cases and the default as well. To solve above problem by usinf Break keyword.
Syntax of Break Statement:
switch(integer expression)
{
case constant 1 :
do this ;
break ;
case constant 2 :
do this ;
break ;
case constant 3 :
do this ;
break ;
default :
do this ;
}