Applications of DBMS
- Many early database applications maintained records in large organizations such as corporations, universities, hospitals, and banks.
- In many of these applications, there were large numbers of records of similar structure. For example, in a university application, similar information would be kept for each student, each course, each grade record, and so on.
- There were also many types of records and many interrelationships among them.
- The World Wide Web provides a large network of interconnected computers.
- Users can create documents using a Web publishing language, such as HyperText Markup Language (HTML), and store these documents on Web servers where other users (clients) can access them.
- Documents can be linked through hyperlinks, which are pointers to other documents.
- One of the most commonly used systems includes Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), which is used to consolidate a variety of functional areas within an organization, including production, sales, distribution, marketing, finance, human resources, and so on.
- Another popular type of system is Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software that spans order processing as well as marketing and customer support functions.
- These applications are Web-enabled in that internal and external users are given a variety of Webportal interfaces to interact with the back-end databases.
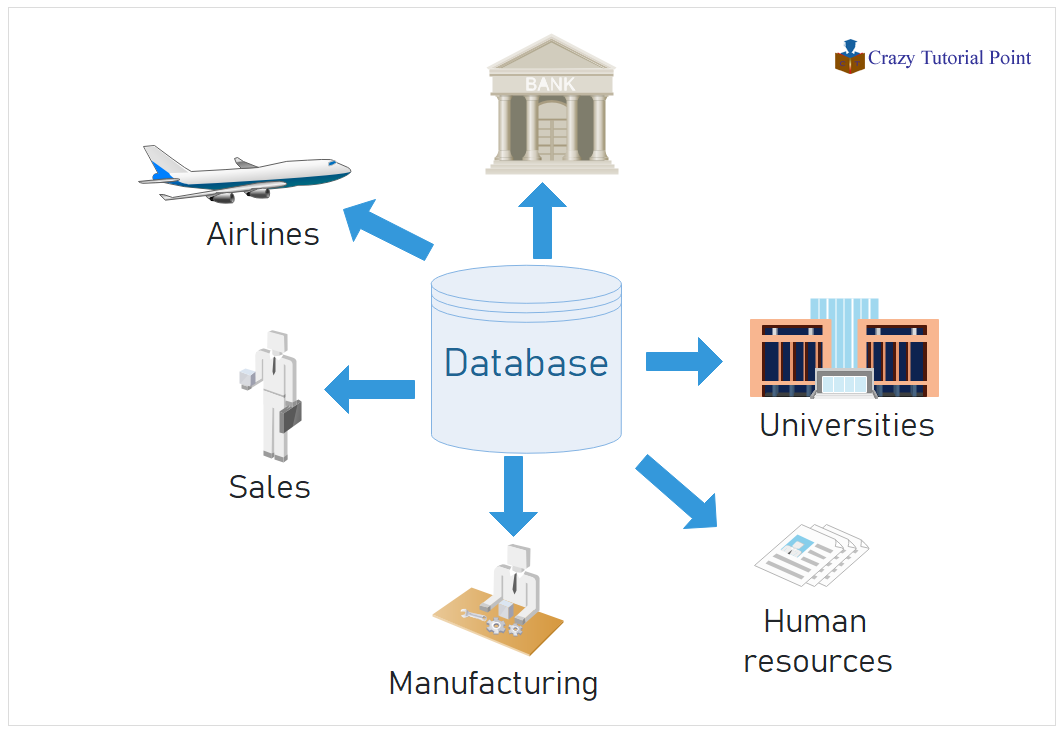
- Banking: all transactions
- Airlines: reservations, schedules
- Universities: registration, grades
- Sales: customers, products, purchases
- Manufacturing: production, inventory, orders, supply chain
- Human resources: employee records, salaries, tax deductions