if statement in c++ example program
- If the conditional expression is true, the target of the if will be executed; otherwise, the target of the else, if it exists, will be executed. At no time will both be executed.
- The conditional expression controlling the if may be any type of valid C++ expression that produces a true or false result.
- If the Boolean expression evaluates to true, then the block of code inside the 'if' statement will be executed.
Syntax of if statement:
if (condition/boolean expression)
{
//Block of C++ statements here
//These statements will only execute if the condition is true
}
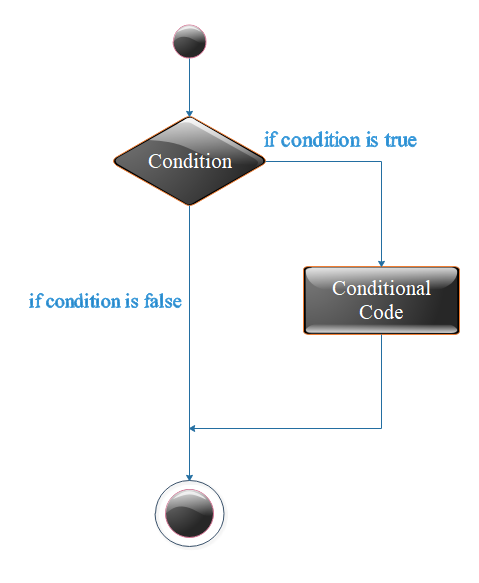
In this statement, if condition is true then statement are execute and if is false, then statement are not execute.
Flow Diagram
Example
// ifdemo.cpp
// demonstrates IF statement
#include using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x;
cout > x;
if( x > 100 )
cout << “That number is greater than 100
”; return 0;
}
Output:
Enter a number: 2000 That number is greater than 100
Nested ifs
- A nested if is an if statement that is the target of another if or else. Nested ifs are very common in programming.
- The main thing to remember about nested ifs in C++ is that an else statement always refers to the nearest if statement that is within the same block as the else and not already associated with an else.
Syntax
if(i)
{
if(j) result = 1;
if(k) result = 2;
}